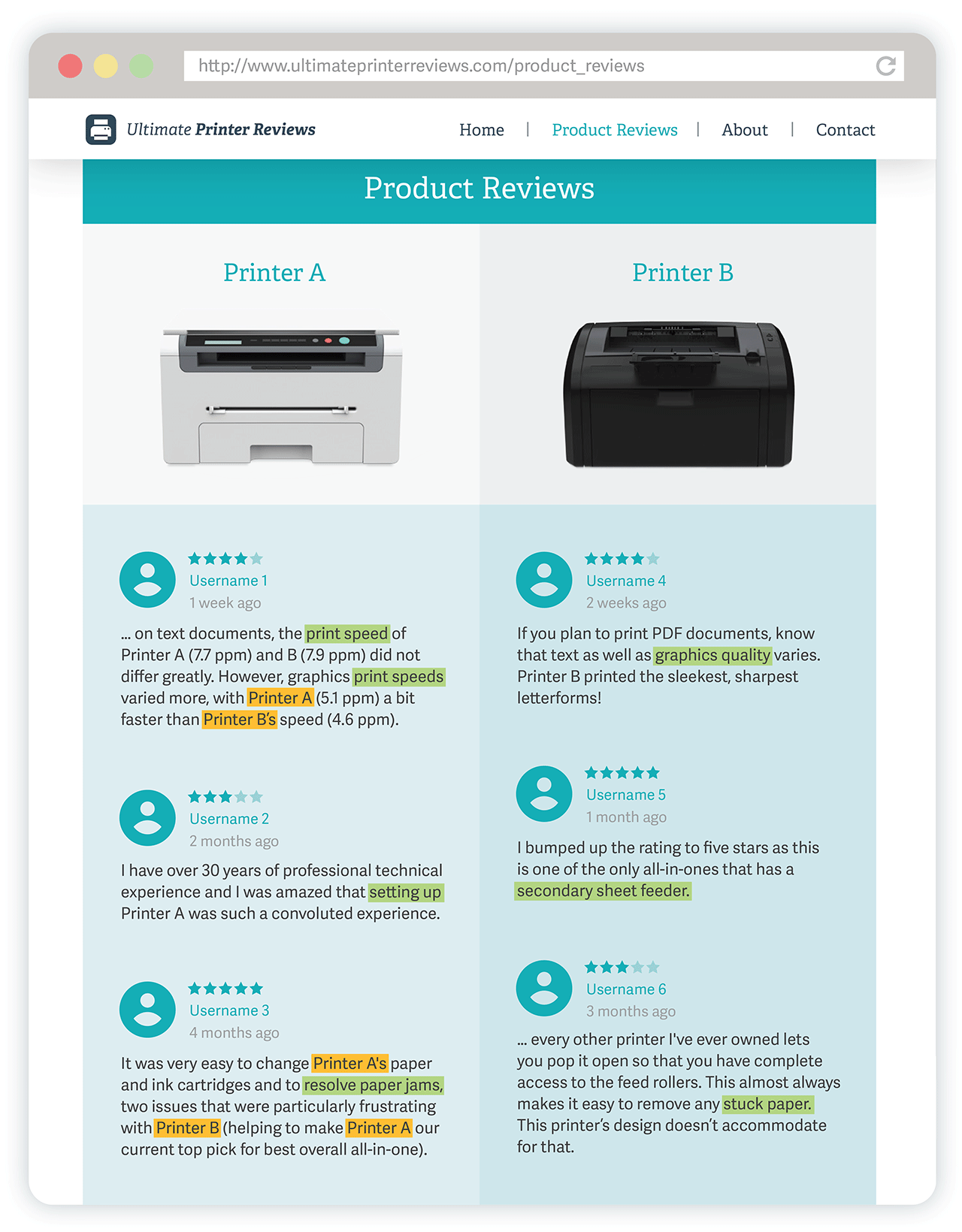
Click graphic to view a larger version
Yellow highlighting: Features of Printer B are discussed in reviews about Printer A, suggesting that the two products may compete in the same market.
Green highlighting: NLP algorithms extract information about important features that are discussed – such as speed, print quality, setup, and secondary sheet feeders – and then assess their relative importance.
How Data Scientists Can Leverage Online Reviews in IP and Antitrust Disputes
The exponential growth of user-generated data is yielding new insights into how products compete with one another.
Product disputes related to intellectual property often introduce questions about a product’s relevant market and the importance of certain product features. Consider a hypothetical dispute between two printer companies.
The manufacturer of Printer A seeks damages because it alleges that the manufacturer of Printer B is infringing on its patent. As a counterargument, Printer B’s manufacturer claims that the features that are allegedly infringed are worth very little to the consumer. Furthermore, it argues that imposing large royalties would drive Printer B out of the market and create potential antitrust concerns. Many traditional measures used to assess the value of the features at issue appear inconclusive; how can data science help?
Companies can use data science tools to leverage user-generated data and find answers to questions that have previously been elusive. In this example, NLP can be used to examine product review websites or other user-generated content related to the printers. Using data science to gather and analyze these kinds of unstructured data can lead to a more sophisticated understanding of consumers’ buying behavior, providing quantifiable insights as to the relative value of the features at issue and whether Printer A and Printer B are considered substitutes for one another in the relevant market. ■