-
Bringing Precision Medicine to Market
Important breakthroughs have occurred in the area of precision medicine in the past several years.
Precision medicine tailors the treatment for a disease to the particular patient’s genetic makeup, environment, and lifestyle, with the goal of selecting the treatments that are more likely to result in patient benefit compared with a “one size fits all” approach. It is a rapidly growing space with projected valuations of global industry size approaching $100 billion by 2024. (See figure.)
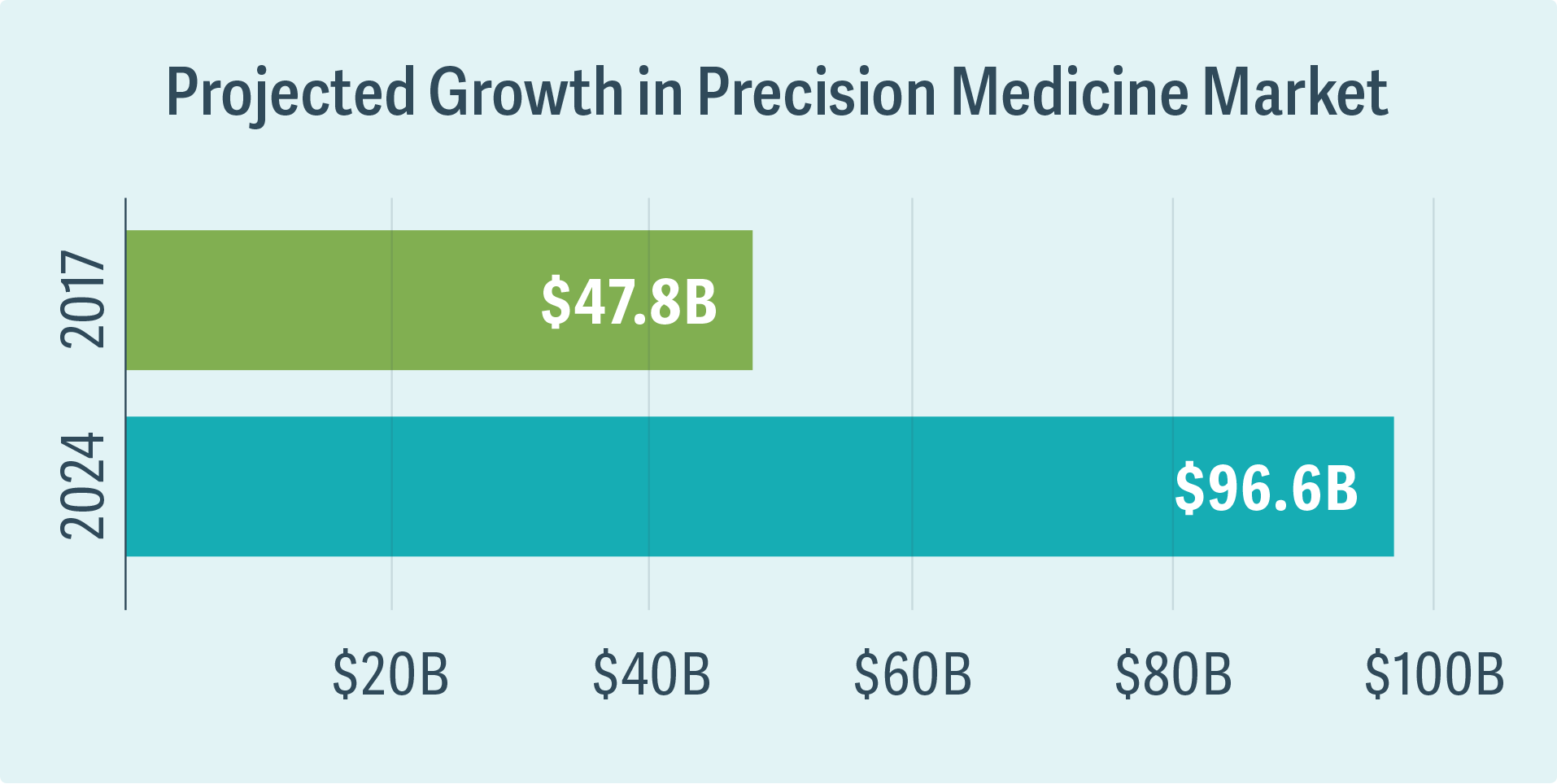
Source: Global Market Insights, Precision Medicine Market Trends 2018–2024 Industry Growth Forecast (October 2017)
Recently, Analysis Group supported Foundation Medicine in its request for a National Coverage Determination (NCD) for FoundationOne CDx™, the first comprehensive genomic profiling assay for solid tumors reviewed in parallel by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) and the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The final NCD, issued by CMS, allows patients to receive FDA-approved next-generation sequencing (NGS) tests for any recurrent, relapsed, refractory, metastatic, or advanced stage III or IV cancer. These tests can be used to sequence the DNA from tumor tissue, allowing care providers to test for a large number of genomic alterations that are implicated in cancer cell biology. An Analysis Group team supported the request with a comprehensive review and synthesis of medical and scientific information on advanced cancer and care settings in which FoundationOne CDx is expected to be used, the analytic and clinical validity of the test, and the clinical utility of NGS-based testing.
Because targeted treatments are often significantly more expensive than those that are not, payers and national health services are increasingly calling for specific benchmarks for comparative efficacy and cost-effectiveness before including them in coverage policies. This consideration, in turn, raises questions about the definition and measurement of value, as well as the possibility of new payment models. Tools from the fields of economics, epidemiology, biostatistics, and health policy can be jointly deployed to address these questions.
For example, Kymriah® (tisagenlecleucel) is a Novartis treatment for pediatric and young adult patients with relapsed or refractory acute lymphoblastic lymphoma (ALL). Kymriah is a CAR-T therapy, with each treatment made from a patient’s own white blood cells. Because the production of each treatment is individualized and only needs to be administered once in a patient’s lifetime, value-based pricing is critical. Analysis Group worked with Novartis to construct a cost-effectiveness model for evaluating value-based prices of Kymriah under different willingness-to-pay thresholds. Our model was also adapted to support Novartis’s submission to the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) in the UK, where Kymriah secured a positive recommendation for reimbursement in ALL. ■
Eric Q. Wu, Managing Principal